Container Technology Wiki
Docker Containers
- Docker 101
- Basic Docker Operations
- Docker Administration
- Docker Security Resources
- Docker OS Interaction
- Docker With Other Tools
- Docker API
- Docker Compose
Kubernetes Guide
- Kubernetes 101
-
Kubernetes Architecture
- Kubernetes Ecosystem
- Kubernetes Nodes
- Kubernetes Pods
- Kubernetes Controllers and Control Plane
- Kubernetes DaemonSets
- Container Runtime Interface
- Working with Containers in Kubernetes
- Working with Images in Kubernetes
- Workloads in Kubernetes
- Kubernetes Services
- Kubernetes Jobs
- Kubernetes and Microservices
- Kubernetes Operators
- Kubernetes Persistent Volumes
- Kubernetes Advantages and Use Cases
-
Kubernetes Operations
- Installing Kubernetes
- Kubernetes Configuration
- Kubernetes Monitoring
- Kubernetes Debugging and Troubleshooting
- Kubernetes Load Balancing
- Kubernetes Security
- Kubernetes Networking
- Kubernetes Storage Management
- Kubernetes in Production
- Working with Kubernetes Ingress
- Kubernetes Security Best Practices
- Managing Kubernetes with Kops and Kubeadm
- Kubernetes Secrets
- Kubernetes Autoscaling
- Kubernetes ConfigMap
- Kubernetes Namespace
- Kubernetes Authentication
- Kubernetes Vault
- CIS Kubernetes Benchmark
- Kubernetes Cluster
- Kubernetes as a Service
- Managed Kubernetes
- Kubernetes Distributions
- Enterprise Kubernetes
Container Basics
- Container Architecture
- Advantages of Containers
- Container Challenges
- Containers and IT Infrastructure
- Enterprise DevOps
- eBPF
- eBPF Linux
Containers Ops
- Container Security Management
- Container Deployment
- Container Monitoring
- Container Automation
- Container Multitenancy
- Container Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Prometheus Monitoring
Container Security
- Container Security Best Practices
- Containers for DevSecOps
- Container Vulnerabilities and Threats
- Container Vulnerability Scanning
- Container Secrets Management
- Container Access Control
- Container Audits and Compliance
- Application Whitelisting
- Zero Trust Networks
- Network Segmentation for Containers
- Container Isolation
- Open Source Security Tools for Containers
- Open Source Vulnerability Scanner
- Open Source Security Tools
- Container Security Tools
Cloud Native Computing Foundation
- AWS EC2 Security
- Cloud-Native Applications
- Cloud-Native Architecture
- Cloud Native AWS
- Cloud Native Development
- Cloud Native Infrastructure
- Cloud Native Security
- Envoy Proxy
- Harbor Kubernetes
- Open Policy Agent
- Oracle Cloud Security
- SaaS Cloud Security
- Security Issues in Cloud Computing
- SPIFFE
- VMware Tanzu
Serverless Computing
- Serverless Architecture
- AWS Lambda
- Azure Functions
- Google Cloud Functions
- Serverless Security
- On-Premises Serverless Platforms
- Function as a Service - FaaS
- Knative
- Serverless vs Containers
Container Platforms
- Containers and Cloud Computing
- Container Operating Systems
- Red Hat Openshift
- Pivotal Container Service
- Multi-Cloud Strategy
- Kubernetes vs Cloud Foundry
- CWPP
Other Container Engines
Kubernetes Alternatives
Container Community and Events
- Container Technology Wiki
- Kubernetes Guide
- Kubernetes Cluster
- Working with Kubernetes Dashboard
Working with Kubernetes Dashboard
Kubernetes Dashboard is a general purpose, web-based UI for Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to manage applications running in the cluster and troubleshoot them, as well as manage the cluster itself. This page gathers resources on how to install, access and secure Kubernetes dashboard.
Below we have compiled publicly available sources from around the world that present views on Working with Kubernetes Dashboard.
The Container Security book by Liz Rice
Fundamental Technology Concepts that Protect Containerized Applications
Perspectives on Working with Kubernetes Dashboard
Kubernetes Dashboard Deep Dive
In this blog, you will get familiar with the Kubernetes Cluster UI Dashboard and with the various components that are pre-deployed in your sandbox environment.

kubernetes.io

On Securing the Kubernetes (Dashboard)
blog.heptio.com

Single Sign-On for Kubernetes: Dashboard Experience
thenewstack.io
how to
The Ultimate Guide to the Kubernetes Dashboard: How to Install and Integrate Metrics-server
Metrics-server replaces Heapster as the primary cluster-wide metrics aggregator for Kubernetes with an integration into the Kubernetes dashboard. In this blog post, we will go through the process of installing and integrating metrics-server into the Kubernetes dashboard.

Kubernetes Dashboard Installation
github.com

How to Install Kubernetes Dashboard
educba.com
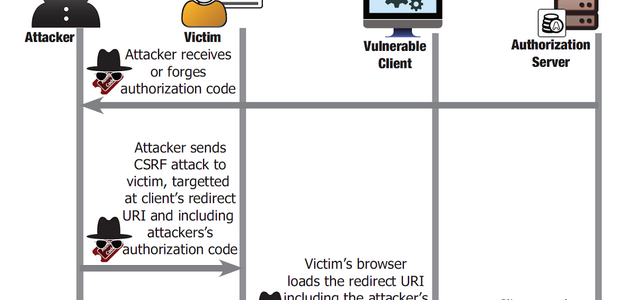
Persistent XSRF on Kubernetes Dashboard using Redhat Keycloak Gatekeeper on Microsof Azure
blog.intothesymmetry.com

Installing the Kubernetes Dashboard
docs.giantswarm.io

Steps to Install Kubernetes Dashboard
assistanz.com
See our comprehensive list for more Kubernetes Tutorials
Specific Environments

Tutorial: Deploy the Kubernetes Dashboard to Amazon EKS Cluster
docs.aws.amazon.com

Manage Kubernetes Dashboard with Azure Kubernetes Service
docs.microsoft.com
Downloads and Add-Ons
Further Reading
Kubernetes Cluster Policies —For enterprise production deployments of Kubernetes clusters, enforcing cluster-wide policies to restrict what a container is allowed to do is an extremely important requirement. This page gathers resources about Kubernetes Cluster Policies such as Pod Security Policies, Network Policies and Resource Quotas.
Kubernetes Federation — Kubernetes Federation gives you the ability to manage deployments and services across all the Kubernetes clusters located in different regions. This page gathers resources on how to set up a Kubernetes Cluster Federation, including tutorials and examples.
Kubernetes High Availability Clusters — Kubernetes clusters enable a higher level of abstraction to deploy and manage a group of containers that comprise the micro-services in a cloud-native application. This page gathers resources about high availability cluster components and how to set up a high availability Kubernetes cluster.
Kubernetes Logging — Application and system logs can help you understand what is happening inside a cluster. Kubernetes provides two logging end-points for applications and cluster logs: Stackdriver Logging for use with Google Cloud Platform and Elasticsearch. This page gathers resources about Kubernetes logging architecture including tutorials and examples.
Kubernetes Proxies — There are several different proxies you may encounter when using Kubernetes: kubectl, apiserver proxy, kube-proxy, a proxy/load-balancer in front of apiserver and a cloud load balancer on external services. This page gathers resources about the different types of Kubernetes proxies.
Kubernetes Serverless — he idea behind serverless computing is that it lets you, as a developer, focus only on writing your code. With serverless computing, you just upload the code somewhere, and it runs whenever you invoke it. Simply put, serverless computing frees you from the complexities of configuring and maintaining Kubernetes clusters. •This page gathers resources about how to build a Serverless Kubernetes cluster.
Working with Kubernetes Dashboard — Kubernetes Dashboard is a general purpose, web-based UI for Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to manage applications running in the cluster and troubleshoot them, as well as manage the cluster itself. This page gathers resources on how to install, access and secure Kubernetes dashboard.
Get updates on container technology





